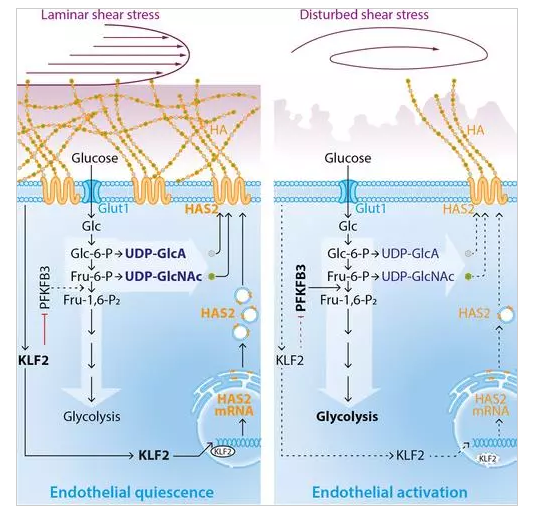
內皮細胞糖萼的主要結構成分是透明質酸(HA)。HA是由UDP-葡萄糖胺(UDP-GlcNAc)和UDP-葡萄糖醛酸(UDP-GlcA)在質膜內表面合成的一種非常長的多糖。HA由合成酶HAS1(透明質酸合成酶1)、HAS2(透明質酸合成酶2)或HAS3(透明質酸合成酶3)合成,并分泌到細胞外空間。這3種亞型在酶的穩定性、HA的延伸率和HA底物的親和力方面存在差異,5種亞型可能影響HA的合成。HAS2是哺乳動物中與HA分布相關的最廣泛的亞型。6只HAS2基因敲除小鼠由于心血管發育的主要缺陷在妊娠早期死亡,推測HAS2以20單糖/s的速率聚合UDP-GlcA和UDP-GlcNAc,5使合成嚴重依賴于這些底物的胞漿可用性。UDP-GlcA and UDP-GlcNAc are derived from respectively the glucuronic acid and hexosamine biosynthesis pathways. We therefore postulated that endothelial HA, and hence glycocalyx thickness, would depend upon endothelial glucose metabolism. It has been shown that, in this respect, endothelial cells are characterized by a high glycolytic flux, where the possibility for glucobiosynthesis can be postulated to be regulated by this flux. Interestingly, the shear stress responsive transcription factor KLF2 has been shown to inhibit PFKFB3 (6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2,6-Biphosphatase 3),8 the key enzyme that drives (hyper)glycolysis.UDP-GlcA和UDP-GlcNAc分別來源于葡萄糖醛酸和己糖胺的生物合成途徑。因此,我們假設內皮細胞的HA和糖萼的厚度將依賴于內皮細胞的葡萄糖代謝。已經證明,在這方面,內皮細胞具有高糖酵解通量的特征,其中糖生物合成的可能性可以假定由該通量調節。有趣的是,剪切應力反應轉錄因子KLF2已經被證明**了PFKFB3(6-磷酸果-2-激酶/果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶3),8-驅動(高)糖酵解的關鍵酶。




 庫存查詢
庫存查詢